diodes weekly
Semiconductors and Diode Theory
- What controls the electrical properties of the atom?
- The valence electron is referred to as a __________ ?
- When silicon atoms combine to form a solid, they arrange themselves into an orderly pattern called ____________ ?
- When is the result when a diode’s reverse bias is increased?
- Which approximation is generally the best choice because it is easy to use and does not require a computer?
- Much of the information on a manufacturer’s data sheet is obscure and of use only to circuit designers.
- True
- False
- A diode can be effectively checked by what equipment?
- All silicon diodes have a knee voltage of approximately ________.
- A diode is a nonlinear device because the graph of its current versus voltage is:
- The point of intersection, which is called the Q point, represents:
- A silicon diode has a saturation current of 6 nA at 25oC. What is the saturation current at 100oC?
- A 10 V DC power supply is connected in series with a silicon diode and a 1 KΩ resistor. Calculate, load current, load voltage, load power, diode power, and total power.
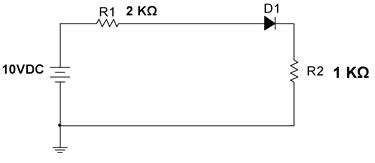
- Figure 1 below shows a DC power supply connected in series with a diode, R1 and R2.
Assume none-ideal diode (VD=0.7 V). Calculate the total current through and voltage across each resistor.